What are ultraviolet (UV) rays?
UV rays are invisible waves of radiation generated by the sun. While some of the sun’s radiation is in the form of visible light and heat, UV rays are shorter in length. This shorter wavelength gives UV its capacity to penetrate into the skin. The one beneficial result is the conversion of vitamin D into its active form. However, UV rays are also just the right length to damage cells and to act as a human carcinogen.
Are there different kinds of UV rays?
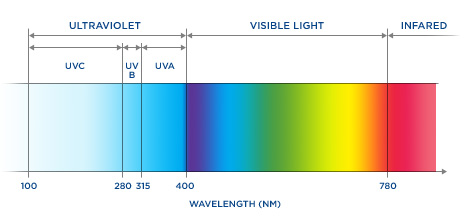
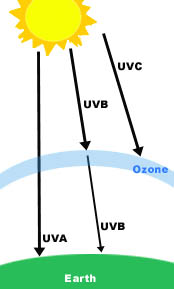
Yes. Ultraviolet radiation is actually a continuous spectrum of wavelengths which scientists have divided into three categories, UVA, UVB, and UVC. Rays with the longest wavelength are designated as UVA. UVB rays are shorter, and UVC rays are the shortest of all. Because ozone in the atmosphere absorbs all UVC and most UVB, 95 percent of the radiation reaching the surface of the earth is UVA while just 5% is UVB. UVB penetrates only into the epidermis (upper layer) of the skin but is the major cause of sunburns. UVA penetrates more deeply, down into the dermis of the skin. Tanning beds emit mostly UVA, however both UVA and UVB are highly damaging and can cause skin cancer.
How do UV rays damage the skin?
When ultraviolet radiation strikes the skin, the rays penetrate beneath the surface and can damage an epidermal cell’s genetic material, or DNA. While the body can usually repair the damage, sometimes this mechanism fails, resulting in a mutation. The skin cancer that can result is named for the type of cell where the mutation occurred. For example, melanoma is a tumor of malignant melanocytes.
UV rays can also damage the dermis and suppress the skin’s immune system, both of which contribute to cancer formation in the epidermis above. Solar damage to the dermal collagen and elastic fibers is a major contributor to skin aging, manifested as wrinkling and sagging.
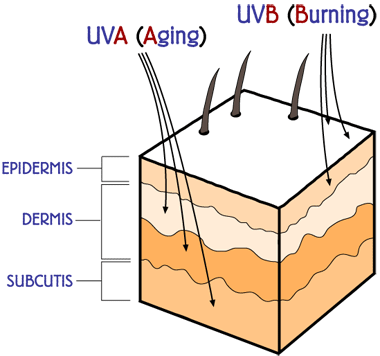
A helpful rule of thumb is: “A (UVA) is for aging, B (UVB) is for burning.” Check out the diagram below for better understanding of UVA and UVB.
When UVB rays penetrate into the skin, they are just the right wavelength to be absorbed by the cell’s genetic material, or DNA. Such bombardment of the DNA can cause it to break apart. While the body can repair most of these molecular injuries, sometimes this mechanism fails, especially in the case of a large dose of radiation, such as a sunburn. This results in mutations which can lead to cancer.
UVA rays penetrate more deeply. They contribute to the formation of skin cancer by inhibiting the tumor suppressive action of the body’s immune cells in the dermis.
In addition to causing skin cancer, damage done by UV exposure includes:
- Sunburn
- Freckles
- Wrinkling
- Dark blotches
- Rough texture
- Skin thinning and sagging
- Cataracts in the eyes
How does the sun cause eye damage?
Overexposure to the sun also can damage your eyes and cause cataracts, macular degeneration and melanoma of the eye. With cataracts, the lens of the eye becomes thick and cloudy, resulting in reduced vision or blindness. According to the World Health Organization, 16 million people worldwide are currently blind as a result of cataracts and as many as 20% of these may be due to UV exposure.
Courtesy Sun Safe Colorado